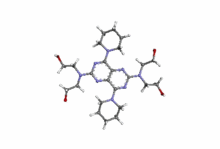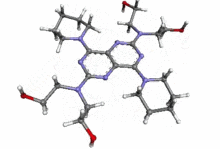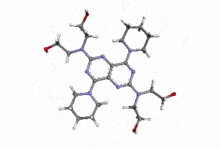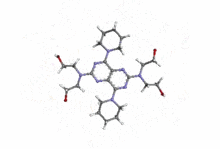
Dipyridamole
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
|
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| 2,2',2'',2'''-(4,8-di(piperidin-1-yl)pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidine-2,6-diyl)bis(azanetriyl)tetraethanol | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Persantine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682830 |
| Pregnancy cat. |
|
| Legal status | |
| Routes | oral, IV |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half-life | Alpha (40 mins), Beta (10 Hours) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 58-32-2 |
| ATC code | B01AC07 |
| PubChem | CID 3108 |
| DrugBank | DB00975 |
| ChemSpider | 2997 |
| UNII | 64ALC7F90C |
| KEGG | D00302 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4653 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL932 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C24H40N8O4 |
| Mol. mass | 504.626 g/mol |
| |
|
Contents
Mechanism and effects
- Dipyridamole inhibits the phosphodiesterase enzymes that normally break down cAMP (increasing cellular cAMP levels and blocking the platelet response to ADP) and/or cGMP (resulting in added benefit when given together with nitric oxide [NO] or statins).
- It inhibits the cellular reuptake of adenosine into platelets, red blood cells and endothelial cells leading to increased extracellular concentrations of adenosine.
Medical uses
- Dipyridamole has been shown to lower pulmonary hypertension without significant drop of systemic blood pressure
- It inhibits formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (MCP-1, MMP-9) in vitro and results in reduction of hsCRP in patients.
- It inhibits proliferation of smooth muscle cells in vivo and modestly increases unassisted patency of synthetic arteriovenous hemodialysis grafts.[2]
- It increases the release of t-PA from brain microvascular endothelial cells
- It results in an increase of 13 - HODE and decrease of 12-HETE in the subendothelial matrix (SEM) and reduced thrombogenicity of the SEM.
- Pretreatment it reduced reperfusion injury in volunteers.
- It has been shown to increase myocardial perfusion and left ventricular function in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy.
- It results in a reduction of the number of thrombin and PECAM-1 receptors on platelets in stroke patients.
- cAMP impairs platelet aggregation and also causes arteriolar smooth muscle relaxation. Chronic therapy did not show significant drop of systemic blood pressure.
- It inhibits the replication of mengovirus RNA.[3]
- It can be used for myocardial stress testing as an alternative to exercise-induced stress methods such as treadmills.
Use in individuals with a history of stroke
Modified release dipyridamole is used in conjunction with aspirin (under the trade names Aggrenox in the USA or Asasantin Retard in the UK) in the secondary prevention of stroke and transient ischaemic attack. This practice has been confirmed by the ESPRIT trial.[4] Dipyridamole absorption is pH-dependent and concomitant treatment with gastric acid suppressors (such as a proton pump inhibitor) will inhibit the absorption of liquid & plain tablets.[5][6] Modified release preparations are buffered and absorption is not affected.[7][8]It is not, however, licensed as monotherapy for stroke prophylaxis, although a Cochrane Review has suggested that dipyridamole may reduce the risk of further vascular events in patients presenting after cerebral ischaemia.[9]
A triple therapy of aspirin, clopidogrel, and dipyridamole has been investigated, but this combination led to an increase in adverse bleeding events.[10]
- Via the mechanisms mentioned above, when given as 3 to 5 min infusion it rapidly increases the local concentration of adenosine in the coronary circulation which causes vasodilation.
- Vasodilation occurs in healthy arteries, whereas stenosed arteries remain narrowed. This creates a "steal" phenomenon where the coronary blood supply will increase to the dilated healthy vessels compared to the stenosed arteries which can then be detected by clinical symptoms of chest pain, electrocardiogram and echocardiography when it causes ischemia.
- Flow heterogeneity (a necessary precursor to ischemia) can be detected with gamma cameras and SPECT using nuclear imaging agents such as Thallium-201, Tc99m-Tetrofosmin and Tc99m-Sestamibi. However relative differences in perfusion do not necessarily imply any absolute decrease in blood supply in the tissue supplied by a stenosed artery.
Other uses
Dipyridamole also has non-medicinal uses in a laboratory context, such as the inhibition of cardiovirus growth in cell culture.Overdose
| Dipyridamole overdose | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| ICD-10 | T46.3 |
| ICD-9 | 972.4 |
| DiseasesDB | 3840 |


No comments:
Post a Comment